Generator Purchase Guide: Hints, Opinions, and the Perfect Models.
Your Generator Purchase Guide – Key Takeaways
- Selecting the right generator type (standby, portable, inverter, or solar) depends on your specific power needs, budget, and intended usage scenarios
- Understanding wattage requirements is crucial—the average home needs 5,000-7,500 watts to power essential appliances during an outage
- Fuel type significantly impacts runtime, maintenance needs, and operational costs, with dual-fuel generators offering the most flexibility
- Modern generators with CO detection technology from PowerGuard Solutions provide enhanced safety features that can prevent dangerous carbon monoxide poisoning
- Regular maintenance extends generator lifespan by up to 15 years, making your investment more valuable in the long run.
Why Your Home Needs a Reliable Generator
Power outages don't announce themselves. When severe weather strikes or the grid fails, having a reliable generator can be the difference between comfort and crisis. In 2022 alone, Americans experienced an average of 8 hours without power, with rural areas seeing significantly longer downtimes. Extended outages can lead to food spoilage, basement flooding, and even dangerous temperature conditions in extreme weather.
Beyond emergencies, generators provide practical solutions for everyday scenarios. They power tools at remote job sites, enable comfortable camping experiences, and allow for energy independence during peak utility hours. PowerGuard Solutions has witnessed firsthand how the right generator transforms homeowners' relationship with energy, providing peace of mind that extends far beyond storm season.
The financial case for generators is compelling as well. While the upfront investment ranges from $400 for portable models to $10,000+ for whole-home standby systems, consider the potential costs of a prolonged outage: hundreds in spoiled food, potential water damage from non-functioning sump pumps, hotel stays, and lost productivity. For many homeowners, a generator pays for itself during just one extended power failure.
- Protection from food spoilage and property damage
- Comfort during extreme weather conditions
- Support for medical devices and essential electronics
- Ability to work from home during grid failures
- Increased property value (for permanent standby installations)
How to Choose the Right Generator Type for Your Needs
Navigating the world of generators starts with understanding the four main types available to homeowners. Your selection should align with your power requirements, budget constraints, and specific usage scenarios. While portable units offer flexibility, standby generators provide comprehensive coverage. Inverters deliver clean power for electronics, while solar options offer eco-friendly alternatives.
The decision matrix extends beyond just power output. Consider factors like noise levels, fuel efficiency, runtime, and installation requirements. A generator that's perfect for occasional camping trips won't necessarily meet your needs during a week-long power outage. Similarly, investing in a whole-house standby generator might be excessive if you simply need to power a few essentials during rare outages.

“8 Types Of Generators for Homeowners | Angi” from www.angi.com and used with no modifications.
Portable Generators: Mobility and Versatility
Portable generators represent the most accessible entry point for backup power, with prices typically ranging from $400 to $3,000. These wheeled units deliver 3,000 to 8,500 watts—enough to keep essential appliances running during an outage. Their primary advantages lie in mobility, storage flexibility, and no permanent installation requirements. Simply wheel it out, connect your appliances via extension cords (or through a manual transfer switch), and pull the starter cord. For those looking to ensure the longevity and efficiency of their generator, it's crucial to address any banging noise issues that may arise, as these can indicate underlying problems.
The tradeoff comes in convenience and capacity. Portable generators require manual startup, regular refueling every 8-12 hours, and outdoor operation at a safe distance from your home. They typically can't power your entire house simultaneously, forcing decisions about which appliances receive precious watts. Despite these limitations, their affordability and versatility make them the most popular choice for occasional outage protection.
Standby Generators: Automatic Backup for Your Entire Home
For comprehensive protection, standby generators represent the gold standard. These permanently installed systems monitor your utility power continuously and activate automatically within seconds of detecting an outage. Connected directly to your home's electrical panel via an automatic transfer switch, they seamlessly power your entire home or selected circuits without any manual intervention. Most models run on natural gas or propane, eliminating the need for refueling during extended outages.
Inverter Generators: Clean Power for Sensitive Electronics
Inverter generators produce “clean” electricity with minimal harmonic distortion, making them ideal for powering sensitive electronics like computers, TVs, and medical equipment. They achieve this through a sophisticated multi-step process that converts AC to DC and back to AC at a consistent frequency. Beyond power quality, inverter models offer significant advantages in fuel efficiency, noise reduction (typically 50-60 decibels versus 65-75 for conventional portables), and compact sizing.
Solar Generators: Eco-Friendly Emergency Power
Solar generators combine photovoltaic panels with battery storage to create a fuel-free power solution. These systems capture sunlight, convert it to electricity, and store it in a battery for later use. Their operation produces zero emissions, zero noise, and zero fuel costs. The latest models offer impressive capacity, with premium units like the Bluetti AC200MAX providing 2,000W output and 2,048Wh of storage—enough to run a refrigerator for 24+ hours or charge a laptop 16+ times.
“13 Types of Generators and Their Uses …” from www.bigrentz.com and used with no modifications.
Understanding Generator Power Ratings
Generator power ratings represent the critical metric determining what you can actually power during an outage. Measured in watts, this specification tells you how many devices can operate simultaneously. For context, a typical 3-bedroom home requires 5,000-7,500 watts to power essential appliances like refrigeration, lighting, and heating systems.
Manufacturers list two distinct power ratings: running (or continuous) watts and starting (or surge) watts. The difference is crucial to understand. Running watts represent what the generator can sustain indefinitely, while starting watts indicate the maximum power available for a few seconds to accommodate motor startup surges. A generator might advertise “5,500 running watts, 6,875 starting watts,” meaning it can handle momentary surges up to 6,875 watts but shouldn't exceed 5,500 watts during normal operation. For more information on how to choose the right generator, check out this generator buying guide.
Undersizing your generator leads to frustration and potential equipment damage. When demand exceeds capacity, voltage drops can cause motors to overheat and electronics to malfunction. The circuit breaker on your generator will eventually trip, but not before causing potential harm. Conversely, oversizing wastes money on capacity you'll never use and may cause generators to run inefficiently under light loads.
Wattage Requirements for Common Household Appliances
Understanding the power consumption of your essential appliances is the first step to selecting the right generator. Refrigerators typically require 700-1,200 running watts but may surge to 2,000+ watts at startup. Air conditioners are among the most power-hungry appliances, with a standard 10,000 BTU unit drawing 1,500 running watts and surging to 2,200 watts. Even smaller items add up quickly—a microwave needs 1,000+ watts, while a desktop computer system demands 400-800 watts.
Medical equipment deserves special consideration when calculating your power needs. CPAP machines generally require 200-500 watts, oxygen concentrators need 400-600 watts, and electric beds or lifts can demand 1,000+ watts during operation. If you depend on these devices, build in a 20% buffer beyond their rated consumption to account for variations in power quality and unexpected needs.
- Refrigerator: 700-1,200 running watts (2,000+ starting)
- Sump pump: 800-1,500 running watts (2,400+ starting)
- Well pump: 1,000-2,100 running watts (3,000+ starting)
- Furnace fan: 700-1,200 running watts (2,350+ starting)
- Window AC: 1,200-2,200 running watts (3,500+ starting)
- Lights, phone chargers, Wi-Fi router: 150-300 watts combined
Starting vs. Running Watts: What's the Difference?
The distinction between starting and running watts represents one of the most misunderstood aspects of generator sizing. Motors and compressors—found in refrigerators, pumps, and air conditioners—require a significant power surge (sometimes 3x their running wattage) for 2-3 seconds during startup. Your generator must handle this momentary demand while maintaining adequate power for other continuously running devices.
Think of it like a car's acceleration versus cruising speed. Just as a vehicle needs extra power to go from 0 to 60 mph before settling into an efficient cruising state, motor-driven appliances need that initial push before operating at their standard power consumption. This explains why generators advertise two different wattage ratings, and why the higher “starting watts” number should guide your purchasing decision if you plan to power multiple motor-driven appliances.
How to Calculate Your Total Power Needs
To accurately determine your generator requirements, create a comprehensive appliance inventory with both running and starting watts. Begin by listing essential items that must remain operational during an outage, then add “nice-to-have” devices as budget allows. For each item, note both its continuous power draw and starting surge requirements. Remember that not all devices will start simultaneously, but your generator must handle the largest potential combined load.

“Types of generators | BISON” from www.bisonindustry.com and used with no modifications.
Sample Power Calculation Worksheet
Appliance Running Watts Starting Watts Priority Refrigerator 800 2,200 Essential Sump Pump 1,050 2,400 Essential Furnace Fan 800 2,350 Essential Lights (5-10 bulbs) 250 0 Essential Router/Modem 25 0 Important TV/Entertainment 500 0 Comfort Total: 3,425 4,750* *Assumes largest starting device (sump pump) runs while others are operating
For precise calculations, use a wattage meter to measure actual consumption rather than relying solely on manufacturer specifications. Plug the device into the meter, then connect the meter to your wall outlet to get real-world readings. This approach accounts for efficiency losses and operational variations that generic wattage charts might miss. For devices hardwired into your home's electrical system, consult with an electrician to determine accurate power requirements.
After compiling your list, add a 20% buffer to accommodate unexpected needs and prevent your generator from consistently operating at maximum capacity. Running generators at 80-90% of their rated capacity improves efficiency, extends lifespan, and provides headroom for additional devices. This means if your calculations show 5,000 watts needed, aim for a generator rated around 6,000-6,500 watts.
Top Generator Models Worth Your Money in 2023
After extensive testing and owner feedback analysis, several generators stand out for their reliability, value, and performance across different categories and price points. The models below represent the best balance of power output, fuel efficiency, durability, and user satisfaction. While premium brands command higher prices, their extended warranties and better parts availability often justify the investment for critical backup power applications.
1. Best Overall: Honda EU2200i
The Honda EU2200i consistently earns top marks for its exceptional reliability, quiet operation (48-57 dB), and clean power output (less than 3% THD). This 2,200-watt inverter generator weighs just 47 pounds while delivering enough power to run essential appliances during an outage. Honda's legendary engine starts reliably in all weather conditions and sips fuel at a miserly rate—running up to 8.1 hours on just 0.95 gallons of gasoline when operating at 25% load.
What truly distinguishes the EU2200i is its durability and resale value. While the $1,199 price tag represents a premium over comparable models, owners report trouble-free operation for 10+ years with basic maintenance. The unit's parallel capability allows connecting two generators to double available power, providing upgrade flexibility as your needs change. For homeowners seeking reliable occasional backup without whole-house coverage, this represents the gold standard in portable power.
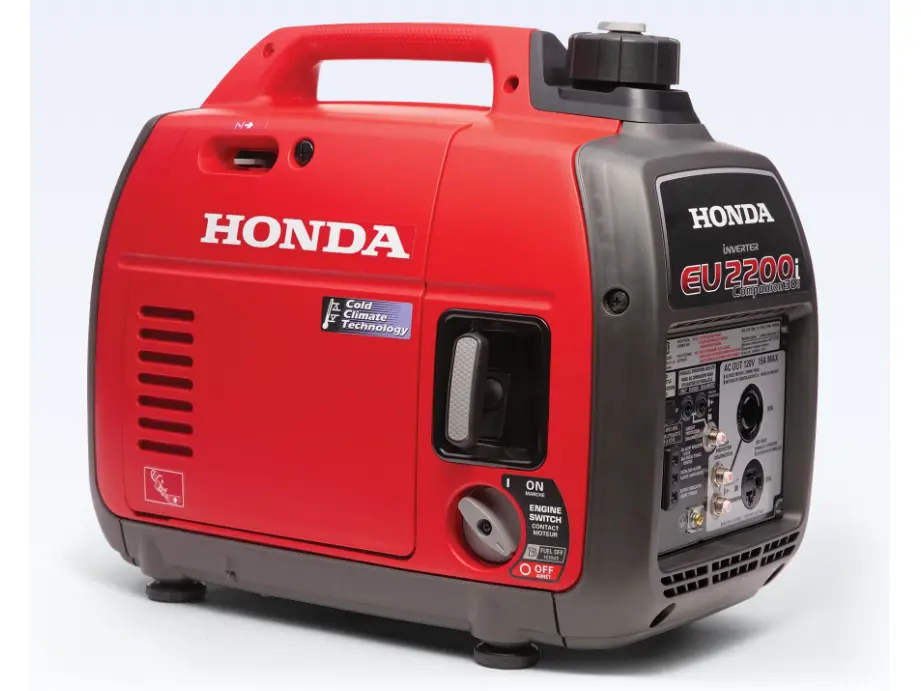

“New 2025 Honda EU2200i Companion in …” from loisellesports.com and used with no modifications.
2. Best Budget Option: Champion 4375-Watt Generator
The Champion 4375-Watt Generator delivers remarkable value at $499, providing 4,375 starting watts and 3,500 running watts—enough to power essential home circuits during outages. This conventional portable generator lacks inverter technology but compensates with raw power, running a refrigerator, lights, and small appliances simultaneously. With a 4-gallon tank, it provides up to 12 hours of runtime at 50% load, impressive efficiency at this price point.
Despite its budget classification, Champion hasn't cut corners on important features. The unit includes low-oil shutdown protection, a convenient hour meter for maintenance tracking, and built-in surge protection. While louder than premium inverters at 68 dB (comparable to a vacuum cleaner), this represents acceptable noise levels for emergency use. Its 3-year residential warranty and accessible nationwide service network provide peace of mind rarely found in economy-priced power equipment.
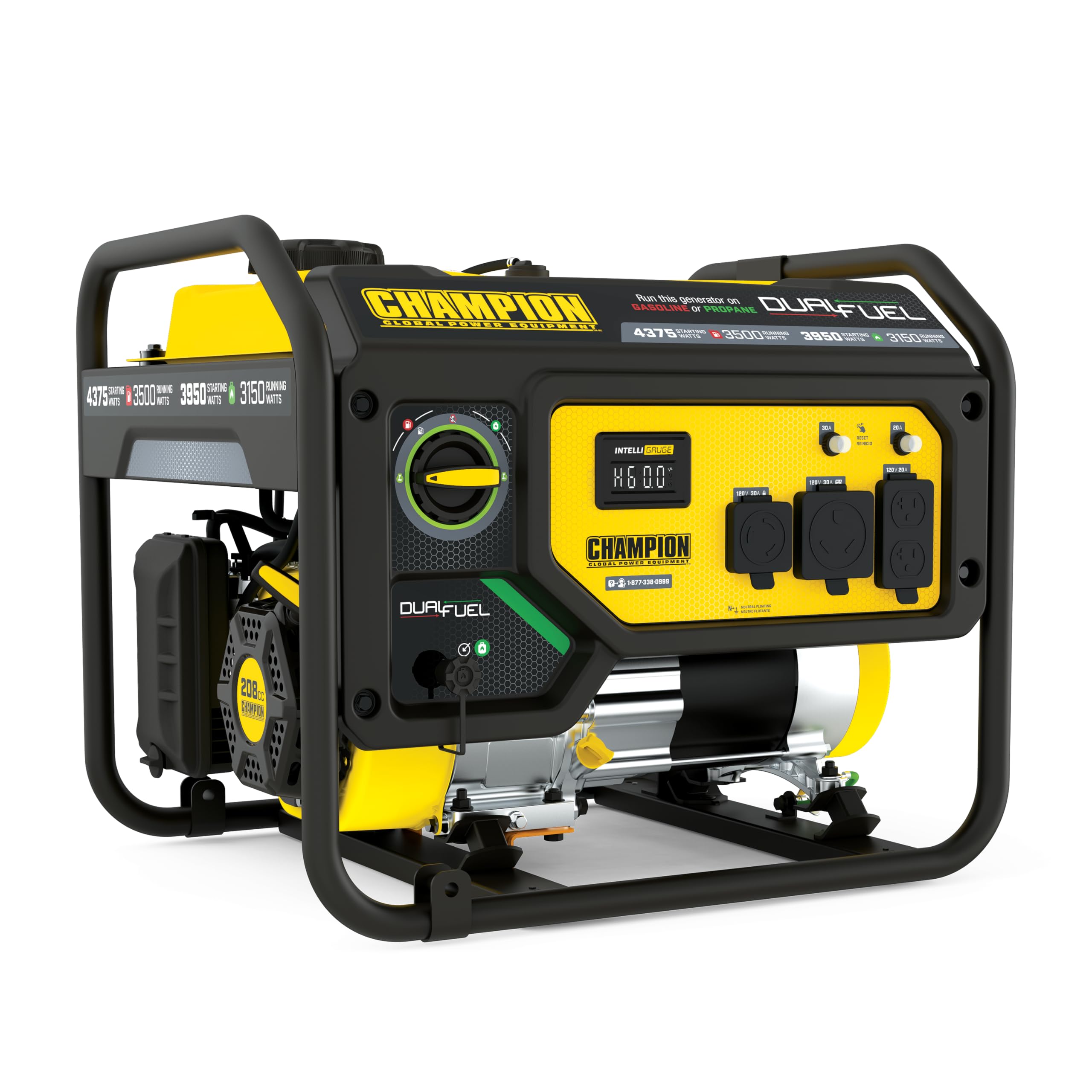

“Champion Power Equipment 4375-Watt …” from www.amazon.com and used with no modifications.
3. Best Standby Generator: Generac Guardian Series
Generac's Guardian Series dominates the standby generator market with models ranging from 10kW to 24kW, suitable for homes of all sizes. The 20kW unit ($4,999 plus installation) represents the sweet spot for most households, capable of powering an entire 3-4 bedroom home including air conditioning and electric appliances. Its proprietary G-Force engine runs on natural gas or propane and starts automatically within 10 seconds of utility power loss, regardless of weather conditions.
What separates the Guardian Series from competitors is Generac's Mobile Link™ remote monitoring system, allowing homeowners to check generator status from anywhere using a smartphone app. The system runs weekly self-diagnostic tests, reporting any issues before they become problems during an actual outage. With a 5-year limited warranty and the largest service network in the industry, Generac provides unmatched peace of mind for those seeking comprehensive power protection.
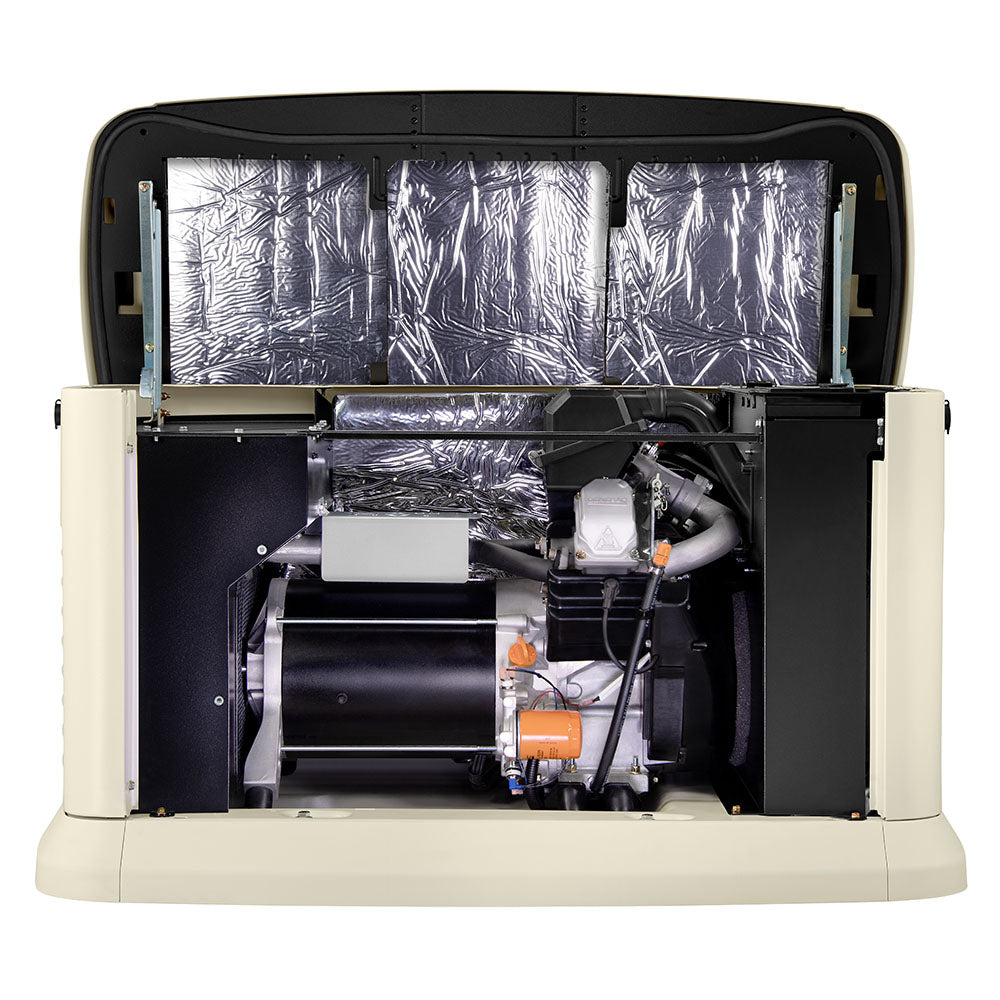

“Generac 7223 14kW Guardian Home Backup …” from www.maxtool.com and used with no modifications.
4. Best Inverter Generator: Westinghouse iGen4500
The Westinghouse iGen4500 strikes an impressive balance between power and portability in the inverter generator category. At 4,500 starting watts and 3,700 running watts, it delivers nearly twice the capacity of comparable Honda and Yamaha models while maintaining competitive fuel efficiency and noise levels. Remote start capability via key fob eliminates the hassle of pull cords, while the intuitive digital display provides real-time feedback on power output, fuel level, runtime, and voltage.
What truly distinguishes this unit is its remarkable 18-hour runtime on a single 3.4-gallon tank when operated at 25% load. This efficiency translates to fewer refueling interruptions during extended outages. At 52 decibels from 23 feet (equivalent to a quiet conversation), it ranks among the quietest generators in its power class. For $949, it offers exceptional value for homeowners needing clean power for electronics while maintaining enough capacity for essential appliances like refrigerators and sump pumps.

“Westinghouse iGen 4500 Inverter …” from www.youtube.com and used with no modifications.
5. Best Solar Generator: Jackery Explorer 1000
The Jackery Explorer 1000 represents the cutting edge of portable solar power, combining a 1,002Wh lithium battery with multiple output options (three AC outlets, two USB-C, two USB-A). This 22-pound unit generates no emissions, requires no fuel, and operates silently—ideal for indoor use during outages. When paired with SolarSaga 100W panels, it recharges completely in 8 hours of sunlight, creating a truly self-sufficient power system for extended emergencies.
While its $1,099 price tag (generator only, panels sold separately) exceeds conventional portable options, the absence of fuel costs and maintenance requirements creates compelling long-term value. The unit excels at powering devices under 1,000 watts, easily handling CPAP machines, laptops, lighting, and communication equipment for 7-10 hours between charges. For eco-conscious homeowners or those prioritizing indoor-safe operation, this represents the most practical entry point to solar backup power.
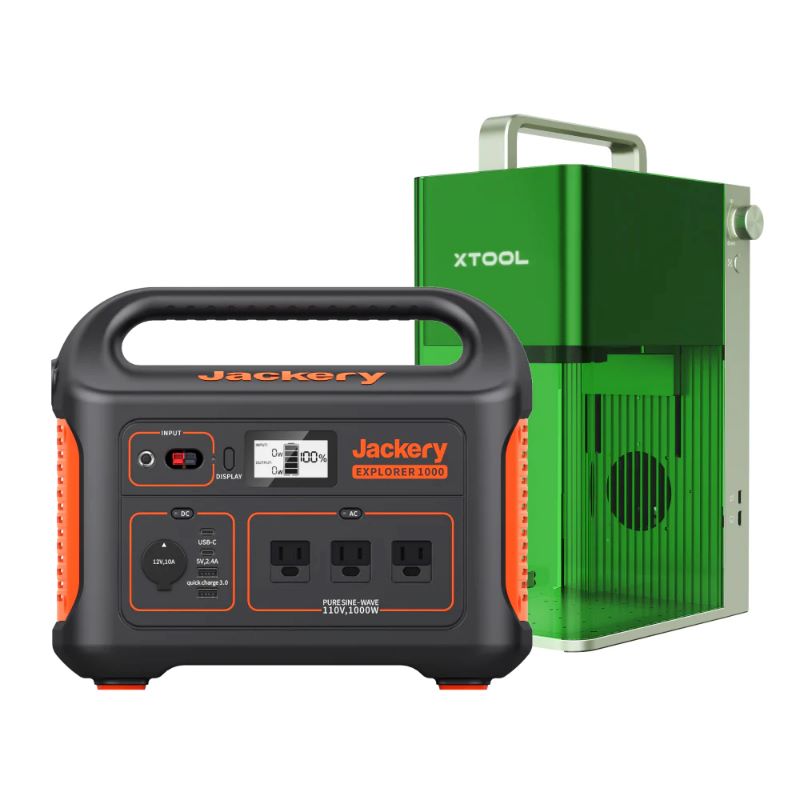

“Jackery 1000 Explorer Power Station …” from thervoutpost.com and used with no modifications.
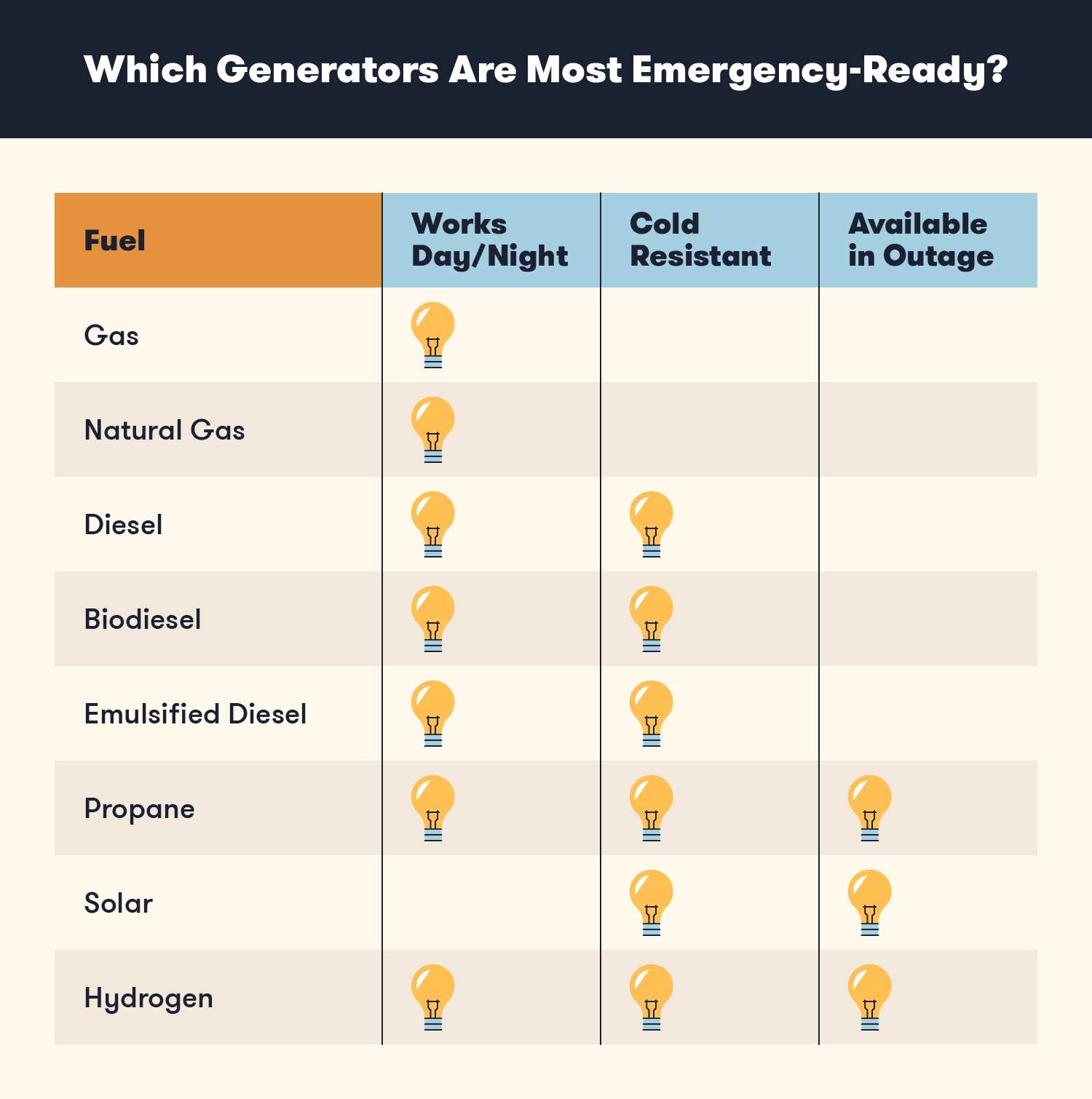
Fuel Types and Runtime Considerations
Your generator's fuel type significantly impacts its convenience, runtime, shelf stability, and operational costs. Each fuel source presents distinct advantages and limitations that should align with your specific backup power strategy. While gasoline offers universal availability, alternative fuels like propane and natural gas provide extended storage life and continuous runtime during prolonged outages.
Gasoline Generators: Pros and Cons
Gasoline remains the most common generator fuel due to its widespread availability and the lower initial cost of gas-powered units. A typical 5,000-watt portable generator consumes approximately 0.75 gallons per hour under full load, providing 5-8 hours of runtime on a standard tank. The primary advantage lies in convenience—during short outages, you likely already have gas on hand or can easily obtain it at thousands of locations.
However, gasoline presents significant drawbacks for emergency preparedness. It degrades within 3-6 months even with stabilizers, making long-term storage problematic. During extended power outages, gas stations often can't operate pumps, creating supply challenges precisely when you need fuel most. Additionally, gasoline generators typically produce more emissions and run louder than alternatives, while presenting greater fire hazards during storage and refueling.
Propane Generators: Clean-Burning Alternative
Propane offers compelling advantages for backup power applications, particularly for extended outages. Unlike gasoline, propane stores indefinitely without degradation, making it ideal for emergency preparedness. A standard 20-pound tank (the size used for grills) provides approximately 5-7 hours of runtime on a 5,000-watt generator at full load, while larger 100-pound tanks extend operation to 25-35 hours without refueling. For more information on preparing for emergencies, you can read this guide on emergency preparedness.
Beyond storage stability, propane burns cleaner than gasoline, producing fewer carbon deposits in the engine and extending generator life. It produces approximately 30% fewer greenhouse gas emissions and significantly reduces toxic components like carbon monoxide. The fuel's lower environmental impact combines with practical benefits—propane tanks remain pressurized during power outages, ensuring fuel availability when gasoline pumps might be inoperable.
Dual Fuel Options: Maximum Flexibility
Dual fuel (or “hybrid”) generators offer the ultimate in flexibility, operating on either gasoline or propane without significant modifications. These units typically feature a selector switch and appropriate connections for both fuel types, allowing users to choose based on availability, runtime needs, or economic considerations. While once considered specialty items, dual fuel technology has become mainstream, with quality options available from Champion, DuroMax, and Westinghouse at minimal price premiums over single-fuel models.
The operational advantages of this approach cannot be overstated. During the initial hours of an outage, you might use gasoline from your vehicle or lawn equipment supply. As the situation extends, switching to propane provides longer runtime without frequent refueling. This redundancy creates a powerful insurance policy against fuel supply disruptions that often accompany major disasters.
Most dual fuel generators deliver approximately 10% less maximum power when running on propane versus gasoline, a reasonable tradeoff for the extended runtime and storage benefits. The conversion efficiency has improved significantly in recent models, with the power differential narrowing to 5-7% in premium units. For most homeowners, this versatility far outweighs minor performance variations between fuel types.
Battery-Powered Solutions: No Emissions
Battery-based power stations represent the newest category in backup power, using lithium-ion technology similar to electric vehicles. These systems produce zero emissions, operate silently, and can be safely used indoors—distinct advantages over traditional fuel-powered generators. Units like the EcoFlow Delta Pro offer 3,600 watt-hours of capacity with 3,600W output capability, enough to run a refrigerator for 15+ hours or charge a laptop 25+ times.
The primary limitation of battery solutions remains their finite runtime without recharging. Unlike fuel generators that run continuously with refueling, battery stations eventually require power input from solar panels, wall outlets, or vehicle charging systems. Premium models mitigate this through expandable battery modules, rapid recharging capabilities, and efficient power management systems that extend functional capacity. For homeowners primarily concerned with short outages and powering essential electronics rather than high-draw appliances, battery stations offer compelling advantages despite their higher cost per watt.
Biogas-Powered Generators
Biogas generators are electrical generators that run on methane-rich biogas, converting organic waste fuel into electricity through internal combustion engines.
How They Work
Modified internal combustion engines burn biogas (50-70% methane) to drive alternators that produce electricity. The system includes gas cleaning, pressure regulation, and safety controls.
Generator Types
Spark Ignition Engines – Modified gasoline engines for 5-500 kW applications. Lower cost but higher maintenance.
Dual-Fuel Engines – Diesel engines running on biogas with pilot diesel injection. 1-5 MW capacity with higher efficiency.
Gas Turbines – For large installations (1-50 MW). High efficiency but require consistent fuel quality.
Performance Specifications
Small units (5-50 kW) achieve 25-35% electrical efficiency. Medium systems (100-1000 kW) reach 30-40% efficiency, while large units (1-10 MW) can achieve 35-45% efficiency. Combined heat and power systems reach 80-85% total efficiency.
Fuel Requirements
Biogas needs 50-65% minimum methane content, hydrogen sulfide below 1000 ppm, and controlled moisture levels. Poor gas quality reduces engine life and performance.
Key Considerations
Capital costs range from $1500-6000 per kW depending on size. Regular maintenance includes oil changes every 500-1000 hours, filter replacements, and annual overhauls. Safety systems include flame arrestors, gas leak detection, and emergency shutoffs.
Installation requires proper ventilation, vibration isolation, and electrical protection systems for safe operation.
Generator Noise Levels: Finding a Quiet Option
Generator noise represents a significant but often overlooked consideration, affecting both user experience and neighborhood relations. The difference between conventional generators (65-85 dB) and quiet inverter models (50-60 dB) is dramatic—a 10 dB increase represents a doubling of perceived loudness. For perspective, normal conversation occurs around 60 dB, while a vacuum cleaner operates at approximately 70 dB. When operating a generator for extended periods, these differences significantly impact comfort and usability.
Decibel Ratings Explained
Generator decibel ratings reflect sound pressure measured at a specific distance, typically 23 feet (7 meters). This standardized approach allows meaningful comparisons between models, though manufacturers sometimes measure under ideal conditions that may not reflect real-world operation. The logarithmic nature of the decibel scale means small numerical differences represent significant perceived changes—a generator rated at 60 dB produces half the perceived noise of one rated at 70 dB. For more information on noise-related issues, explore solutions in this troubleshooting guide.
Load percentage dramatically affects noise output, with most generators running significantly quieter at 25% capacity versus full power. This explains why manufacturers often advertise the lowest possible number, measured at minimal load. For realistic expectations, add 5-7 dB to the rated level when operating at 50-75% capacity, which represents typical usage during an outage.
Your operating environment also influences perceived noise. Hard surfaces like concrete patios or walls reflect and amplify sound, while soft surroundings like grass and shrubs absorb it. A generator rated at 65 dB can easily exceed 70 dB when placed on a concrete pad between buildings, creating a “sound chamber” effect. Consider both placement and potential acoustic modifications like specialized enclosures or sound-dampening mats when noise concerns exist.
Quietest Models on the Market
The Honda EU2200i sets the industry standard for quiet operation at just 48-57 dB depending on load, comparable to a quiet conversation. This exceptional performance comes from a combination of inverter technology, specialized mufflers, acoustic insulation, and Honda's refined engine design. At 2,200 starting watts, it provides sufficient power for essential needs while remaining unobtrusive even in noise-sensitive environments like campgrounds.
For higher power needs, the Westinghouse iGen4500 delivers remarkable sound performance at 52 dB while providing twice the capacity of the Honda. The A-iPower SUA2000iV offers budget-friendly quiet operation at 58 dB with 2,000 starting watts, though with somewhat less refined sound quality than premium brands. Among conventional non-inverter generators, the Champion 6250-Watt Open Frame Inverter represents a significant improvement at 69 dB versus typical models in its class that exceed 75 dB. For those looking to improve their home environment, consider exploring mold testing kits to ensure a safe and healthy space.
Essential Safety Features to Look For
Generator safety features have evolved dramatically in recent years, with manufacturers implementing sophisticated systems to prevent the most common hazards. Carbon monoxide poisoning represents the deadliest risk, with hundreds of generator-related deaths and thousands of injuries occurring during major outages. Modern units increasingly incorporate CO detection, automatic shutdown systems, and educational warnings to mitigate these dangers.
Automatic Low-Oil Shutdown
Low-oil shutdown protection prevents catastrophic engine damage by automatically turning off the generator when oil levels fall below safe operating thresholds. This feature has become standard on nearly all quality generators, from budget portables to premium standby systems. The mechanism uses a float switch or pressure sensor to monitor oil levels continuously during operation, triggering shutdown before metal-on-metal contact can occur in the engine.
Beyond preventing expensive repairs, this safety system eliminates the fire hazard associated with seized engines and overheated components. For maximum protection, look for models with indicator lights that specifically identify low oil as the shutdown cause, distinguishing it from other potential issues. Better units resume operation automatically once oil is added, without requiring complete restart procedures.
Carbon Monoxide Detection
Carbon monoxide detection technology represents the most significant safety advancement in portable generators. Systems like Generac's CO-SENSE and Honda's CO-MINDER use specialized sensors to monitor carbon monoxide concentration around the generator, automatically shutting down the engine when dangerous levels are detected. This technology addresses the leading cause of generator-related deaths, particularly when units are operated too close to living spaces or in partially enclosed areas during inclement weather.
The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has endorsed these systems as effective lifesaving measures, with data showing a significant reduction in CO poisoning incidents when properly implemented. While adding approximately $50-100 to manufacturing costs, this feature provides invaluable protection against an odorless, colorless, and deadly gas that claims hundreds of lives annually during power outages. As awareness grows, CO detection is transitioning from premium feature to essential standard across the industry.
Circuit Protection Systems
Comprehensive circuit protection safeguards both your generator and connected equipment from electrical damage. Quality generators incorporate multi-level systems including overload protection (preventing excessive current draw), short circuit protection (automatically disconnecting when dangerous faults occur), and GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets that prevent shock hazards in wet conditions. These features work together to prevent the most common electrical failures while protecting users from potential injury.
Advanced models add electronic voltage regulation that maintains consistent output regardless of load changes or engine speed variations. This steady power prevents damage to sensitive electronics and extends appliance life by eliminating harmful voltage spikes and sags. When evaluating generator safety systems, examine both the protection mechanisms and the quality of the circuit breakers themselves—premium units use hydraulic-magnetic breakers that respond more precisely than thermal alternatives while proving more reliable in extreme temperatures.
Weather-Resistant Covers and Housing
Weather protection features allow safer operation during adverse conditions when power needs are often greatest. Quality portable generators include covered outlets with rubber seals that prevent moisture intrusion while in use. Better models add special channeling around control panels that diverts water away from sensitive components and GFCI-protected outlets that immediately detect dangerous ground faults that might occur in wet environments.
For standby generators, comprehensive weather-resistant housing protects the entire system from environmental extremes. Premium models use corrosion-resistant aluminum enclosures with automotive-grade paint systems tested to withstand 5,000+ hours of salt spray exposure—particularly important in coastal areas. Advanced designs incorporate specialized airflow patterns that prevent water ingress while maintaining proper cooling, allowing continuous operation even during severe storms that cause the original power failure. If you experience a banging noise from your furnace, it's crucial to address it promptly to ensure your standby generator remains in optimal condition.
Installation and Setup Tips
Proper generator installation significantly impacts safety, reliability, and operating costs over the equipment's lifespan. While portable units require minimal setup, their placement remains critical to prevent noise concerns and manage carbon monoxide infiltration. Standby systems demand professional installation to ensure code compliance, proper fuel connections, and seamless integration with your home's electrical system.
Proper Placement for Safe Operation
Portable generators must always operate outdoors in well-ventilated areas, with current safety guidelines recommending at least 20 feet from any doors, windows, or vents. Position the exhaust facing away from the home, as CO can accumulate along walls and enter through seemingly minor openings. Never operate generators in garages, basements, crawlspaces, or under decks/porches, even with doors or windows open, as carbon monoxide can build to lethal levels within minutes. For those concerned about indoor air quality, consider exploring mold testing kits as an additional safety measure.
Weather protection presents a common challenge, as generators can't operate in rain or snow without specialized covers. Purpose-built generator tents provide weather protection while maintaining proper ventilation, with designs specifically preventing CO accumulation. These structures use flame-resistant materials and maintain safe clearance from hot engine components. Alternatively, permanent structures like generator sheds must include substantial ventilation and maintain required clearances from combustible materials.
Consider noise impact on both your household and neighbors when determining placement. Sound travels differently at night when background noise diminishes, making generator operation more noticeable during typical outage scenarios. Position units away from sleeping areas when possible, using structures or landscape features to absorb sound. Some municipalities have noise ordinances with specific decibel limits, though these are typically waived during declared emergencies.
Transfer Switch Installation
Transfer switches provide the safest and most convenient method for connecting generators to your home's electrical system. These devices prevent dangerous backfeeding (where generator power travels back through utility lines, endangering repair workers) while eliminating the need for multiple extension cords throughout your home. Professional installation costs typically range from $500-1,000 depending on your panel configuration and local labor rates.
For portable generators, manual transfer switches or interlock kits represent the most cost-effective approach. Manual switches allow selecting specific circuits to power, typically 6-10 of your most essential needs. Interlock kits modify your existing electrical panel with a simple mechanical system preventing simultaneous connection to both utility and generator power. Both options require professional installation by licensed electricians to ensure code compliance and safety.
Standby generators require automatic transfer switches that monitor utility power and control generator operation. These sophisticated devices detect outages, start the generator, wait for stable power production, disconnect from utility lines, connect to generator power, and then reverse the process when utility service returns. While more expensive than manual alternatives, they provide true hands-off operation and protect sensitive electronics through controlled power transitions.
Professional vs. DIY Setup
While portable generator setup might seem straightforward, several aspects benefit from professional consultation. Electricians can perform load calculations to verify your generator adequately meets your needs, recommend appropriate transfer switch options, and ensure your home's wiring safely accommodates backup power. For those comfortable with basic electrical concepts, connecting devices directly to generators via extension cords requires no professional assistance, though understanding load management remains essential.
Standby generator installation absolutely requires professional expertise, typically involving licensed electricians, plumbers, and inspectors. These systems integrate with both electrical service and fuel supplies (natural gas or propane), requiring permits and inspections in most jurisdictions. Professional installation includes precise load calculations, appropriate sizing, and programming automatic transfer switches to protect specific circuits based on your priorities and generator capacity.
The cost difference between professional and DIY approaches can be substantial. A typical standby generator installation adds $2,000-4,000 to equipment costs, while professional transfer switch installation for portable units runs $500-1,000. However, improper installation creates significant risks—electrical fires, carbon monoxide poisoning, equipment damage, and voided warranties. For most homeowners, professional installation provides value through safety assurance, code compliance, and system optimization.
Maintenance Guide for Longer Generator Life
Proper maintenance dramatically extends generator lifespan while ensuring reliable operation when you need it most. Unlike continuously operating equipment, generators experience unique stresses from intermittent use, fuel degradation during storage, and operation under varying loads. A well-maintained generator typically lasts 10-15 years for portable models and 15-25 years for standby systems, representing exceptional return on investment for emergency preparedness.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Establish a consistent maintenance schedule based on both runtime hours and calendar time, as generators deteriorate even during periods of non-use. For portable models, change oil every 50-100 operating hours or annually, whichever comes first. Air filters require inspection every 25 hours and replacement when visibly dirty. Spark plugs typically last 100-200 hours but should be replaced annually for emergency equipment regardless of usage to ensure reliable starting.
Standby generators include automated maintenance cycles that periodically run the system to prevent fuel degradation and lubricate engine components. However, these systems still require professional service annually or every 200 operating hours. Maintenance typically includes oil and filter changes, spark plug inspection, fuel system cleaning, battery testing, and electronic diagnostic checks of the transfer switch and control systems.
Fuel Management Best Practices
Proper fuel management prevents the most common generator failures during extended storage. For gasoline generators, add fuel stabilizer at the recommended concentration with every fill-up, not just during seasonal storage. This practice prevents the formation of gummy deposits that clog carburetors and fuel systems. Even with stabilizer, replace gasoline every three months, as its volatile components evaporate and its combustion properties degrade over time.
For extended storage exceeding three months, most manufacturers recommend running the generator until the fuel system is completely dry. This prevents varnish formation in carburetors and fuel lines that can cause starting problems and performance issues. Alternatively, some owners maintain small quantities of stabilized fuel and run the generator monthly for 20-30 minutes under load, which circulates fresh fuel through the system while exercising mechanical components. If you experience any banging noise from your generator, it might be time for some troubleshooting.
Propane and natural gas eliminate most fuel degradation concerns, representing a significant maintenance advantage for these systems. However, their fuel connections require annual inspection for leaks, corrosion, or damage, particularly at regulator fittings and flexible supply lines. Professional technicians use specialized equipment to detect minor leaks that might otherwise go unnoticed during visual inspection.
Winterizing Your Generator
Cold weather presents unique challenges for generator operation and storage. For wintertime readiness, switch to synthetic oil that maintains proper viscosity in low temperatures—conventional oils thicken substantially below freezing, increasing starting difficulty and initial wear. Battery capacity also diminishes in cold weather, with starting power reduced by up to 50% at 0°F compared to 80°F performance. For critical emergency generators, consider battery warmers or bring batteries indoors during extreme cold when the generator isn't needed. If you're experiencing a banging noise from your furnace, it might be time to check your heating system as well.
Real Customer Reviews: What Owners Really Think
Beyond manufacturer specifications and marketing claims, real-world experiences reveal how generators perform during actual emergencies. Analysis of thousands of verified owner reviews across major retailers and specialty forums reveals consistent patterns regarding reliability, usability, and customer support. While individual experiences vary, clear trends emerge that can guide purchasing decisions beyond technical specifications alone.
Reliability Ratings
Honda consistently earns the highest reliability ratings across both professional testing and customer reviews, with 94% of owners reporting trouble-free operation beyond five years. This exceptional performance justifies their premium pricing for many users, particularly those in areas with frequent outages. Generac dominates the standby generator category with 91% satisfaction rates, though some customers report initial setup challenges requiring professional intervention.
Among mid-priced brands, Westinghouse has dramatically improved reliability ratings over the past five years, with current models achieving 89% positive reliability scores. Champion maintains solid performance at lower price points, with 86% of owners reporting satisfaction with reliability, though their units typically require more frequent maintenance than premium brands.
Budget-focused brands show more variation, with A-iPower and DuroMax receiving mixed reliability reviews. Analysis shows their performance strongly correlates with maintenance practices—owners who follow rigorous maintenance schedules report 80%+ satisfaction, while those with irregular maintenance experience significantly higher failure rates of 30-40% within three years.
Generator Brand Reliability Comparison
Brand Reliability Rating Common Praise Common Complaints Honda 94% Easy starting, quiet operation High price, limited availability Generac 91% Automatic operation, power quality Installation complexity, service delays Westinghouse 89% Value for power, feature set Warranty service, parts availability Champion 86% Starting reliability, durability Noise levels, fuel efficiency DuroMax 78% Power output, dual fuel capability Quality control, carburetor issues
Customer Service Experiences
Customer service quality varies dramatically between manufacturers, significantly impacting ownership experience when problems arise. Honda and Yamaha consistently receive praise for their dealer networks and parts availability, with most issues resolved within 1-2 weeks even during high-demand periods following major storms. Generac maintains the largest service network for home standby systems, though customer experiences vary by local dealer quality, with urban areas receiving substantially faster service than rural regions. For those interested in learning more about company's true treasure, understanding the value of long-serving staff can provide additional insights.
Common Complaints and Solutions
Across brands and price points, starting difficulties represent the most common generator complaint, particularly after storage periods. This issue typically results from fuel degradation rather than mechanical failure, with 78% of cases resolved through carburetor cleaning and fresh fuel. Implementing proper fuel management practices—using stabilizers, periodic operation, and complete fuel system drainage before storage—prevents most of these problems. For those experiencing persistent starting issues, upgrading to a model with electronic fuel injection virtually eliminates carburetor-related problems, though at higher initial cost.
Where to Buy Your Generator
Generator purchasing channels significantly impact price, service quality, and long-term support. While online retailers offer competitive pricing and convenient shopping, specialized dealers provide expertise, setup assistance, and ongoing service relationships. The optimal purchasing strategy depends on your technical comfort level, budget constraints, and anticipated service needs. For those concerned about rising costs, it may be wise to prepare for surging costs in the near future.
Online vs. Local Retailers
Online retailers like Amazon, Northern Tool, and Electric Generators Direct typically offer 5-15% lower prices than brick-and-mortar stores, particularly for portable models below $1,500. These savings come from reduced overhead and highly competitive marketplaces that compress profit margins. However, online purchases generally require more self-service in terms of selection guidance, delivery coordination (especially for large units), and warranty claims processing.
Local dealers and specialty stores provide valuable expertise that can prevent expensive mistakes in sizing and selection. Their staff can perform load calculations, recommend appropriate models based on your specific needs, and often provide delivery and basic setup assistance. While their prices typically run higher than online alternatives, many offer price matching against major online retailers, effectively providing expertise at minimal premium.
For standby generators, local professional dealers offer significant advantages over both big-box retailers and online sources. These specialists provide comprehensive services including site evaluation, permit handling, professional installation, and ongoing maintenance programs. Many maintain service priority systems that give their customers precedence during high-demand periods following major outages—a benefit worth considerable premium when emergency service is needed.

Best Times to Purchase for Maximum Savings
Generator pricing follows predictable seasonal patterns, with the best values typically available during December-February and June-July. These periods represent inventory transition times and lower demand cycles, with discounts averaging 15-25% below peak season pricing. Conversely, prices typically spike following major weather events and during September-November hurricane season, when demand surges and inventories tighten across all distribution channels.
The Final Verdict: Investing in Peace of Mind
A quality generator represents more than emergency equipment—it provides genuine peace of mind during increasingly unpredictable weather patterns and grid vulnerabilities. While the initial investment ranges from $500 for basic portable models to $10,000+ for comprehensive standby systems, this cost amortized over a 10-15 year lifespan represents exceptional value compared to the potential losses from even a single extended outage. PowerGuard Solutions helps thousands of homeowners find their ideal backup power solution each year, ensuring families maintain comfort, safety, and security regardless of external circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to the most common questions prospective generator owners ask before making their purchase. These responses address typical concerns about costs, operation, safety, and maintenance that arise during the selection process.
How much does a whole-house generator typically cost?
Whole-house standby generators typically cost between $6,000 and $15,000 installed, depending on capacity, features, and installation complexity. A 20kW unit sufficient for a 2,500 square foot home averages $8,500-$11,000 including standard installation. This price encompasses the generator ($4,000-$6,000), automatic transfer switch ($500-$1,500), concrete pad ($300-$500), and professional installation ($2,000-$4,000). Additional costs may include upgrading gas lines, electrical panel modifications, permits, and extended warranties.
Can I run my generator in the rain?
Standard portable generators should never operate directly in rain or snow due to electrocution hazards and potential equipment damage. Manufacturers specifically warn against wet weather operation in owner's manuals, and doing so typically voids warranties. Safe alternatives include operating under purpose-built generator tents/covers specially designed to provide weather protection while ensuring proper ventilation, or constructing permanent structures with appropriate clearances for heat, exhaust, and airflow. Standby generators feature weather-resistant housings specifically engineered for all-weather operation without additional protection.

How often should I test my standby generator?
Manufacturers recommend exercising standby generators under load for 20-30 minutes every month to maintain optimal performance. Most modern units perform this function automatically according to programmable schedules, typically during weekday afternoons when power demands are lower. This regular operation circulates fresh oil through the engine, prevents fuel system deposits, recharges the starting battery, and identifies potential issues before emergency situations. Professional annual maintenance remains necessary regardless of self-test schedules, as certain inspections and fluid changes cannot be automated. For more on professional maintenance solutions, check out our detailed guide.
What's the difference between a transfer switch and an interlock kit?
Transfer switches and interlock kits both prevent dangerous backfeeding of generator power into utility lines, but they operate differently and offer distinct advantages. A transfer switch is a separate device that connects between your electrical panel and selected circuits, allowing you to power specific loads without accessing the main panel during outages. An interlock kit modifies your existing electrical panel with a mechanical system that physically prevents engaging both utility and generator breakers simultaneously, requiring manual switching during power transitions. For those considering home safety upgrades, understanding the pros and cons of DIY vs professional solutions can be beneficial.
Transfer Switch vs. Interlock Kit Comparison
Feature Transfer Switch Interlock Kit Typical Cost $500-$1,000 installed $200-$400 installed Circuit Selection Limited to pre-wired circuits Any circuit in panel Ease of Use Simple labeled switches Requires breaker knowledge Installation Complexity Moderate – separate mounting Simple – modifies existing panel Load Management Visual indicators on switch Requires manual calculation
Transfer switches offer superior convenience and safety, particularly for households where not all members understand electrical systems. Their clearly labeled switches simplify operation during stressful outage situations. Interlock kits provide greater flexibility by allowing access to any circuit in your panel rather than just pre-selected ones, but require more user knowledge to prevent overloading the generator.
For portable generators under 8,000 watts, manual transfer switches typically represent the best balance of safety, convenience, and cost. Larger portable units and all standby generators benefit from automatic transfer switches that eliminate manual intervention entirely, though at substantially higher cost.
How long do generators typically last?
Generator lifespan varies significantly based on type, quality, maintenance practices, and usage patterns. Portable generators typically last 1,000-2,000 operating hours when properly maintained, translating to 10-15 years of typical homeowner emergency use. Premium inverter generators often achieve the higher end of this range due to advanced electronic engine management systems that optimize operation. Budget conventional generators typically fall toward the lower end, particularly when maintenance is inconsistent.
Standby generators are designed for longer service lives, typically 2,500-3,000 hours or 15-25 years in residential applications. Their commercial-grade engines, sophisticated cooling systems, and automatic maintenance cycles contribute to this extended durability. The most common component failure in standby systems is the automatic transfer switch rather than the generator itself, as this device contains complex electronics and mechanical relays that experience wear with each power transition.
Actual calendar lifespan depends primarily on maintenance quality rather than initial purchase price. Analysis of warranty claims shows that 80% of premature failures result from maintenance-related issues—primarily fuel system problems, oil starvation, and cooling system restrictions. Following manufacturer-recommended service schedules and proper storage protocols typically doubles effective lifespan compared to neglected units, regardless of price point or brand reputation. For more insights on maintenance, you might find this troubleshooting guide helpful.
When it comes to home heating systems, unexpected noises can be alarming and indicate underlying issues. If you're experiencing a banging noise from your furnace, it might be time to address potential problems. For comprehensive solutions and a detailed troubleshooting guide, check out our article on banging noise from furnace solutions.




