Life expectancy in the US stays below the record high of 2014 according to 2017 published data. The long term longevity trend as science improves the health of the nation and preserves lives, appears to have ceased.
Life Expectancy in US by State
Life expectancy in some states increased by just three years since 1980, and by as much as nine years in others. These variations are closely related to differences in a host of factors. For example, long-standing research has found that Americans with lower socioeconomic status tend to have lower life expectancies than more affluent Americans.
Life expectancy at birth in Mississippi is the lowest of all states and has historically been low. As is generally the case in states with low life expectancy, Mississippi struggles with poverty, and residents report relatively unhealthy behaviors. At 19.8 percent, no state has a higher poverty rate. Mississippi also has the largest share of adults who do not exercise, at more than a third of the local adult population.
Similar to other states with the shortest life expectancies, Alabama struggles with poverty, and residents report relatively unhealthy behaviors, such as adult obesity, physical inactivity, and smoking. via usatoday.com
Falling behind: expectancy in US counties from 2000 to 2007 in an international context
” they argue that to understand shifts in inequality of life expectancy in the last 30 years or so, one needs to draw distinctions by age group. From their abstract:. “focusing on groups of counties ranked by their poverty rates, we show that gains in life expectancy at birth have actually been relatively equally distributed between rich and poor areas. Turning to an analysis of age-specific mortality rates, we show that among adults age 50 and over, mortality has declined more quickly in richer areas than in poorer ones, resulting in increased inequality in mortality. This finding is consistent with previous research on the subject. However, among children, mortality has been falling more quickly in poorer areas with the result that inequality in mortality has fallen substantially over time.
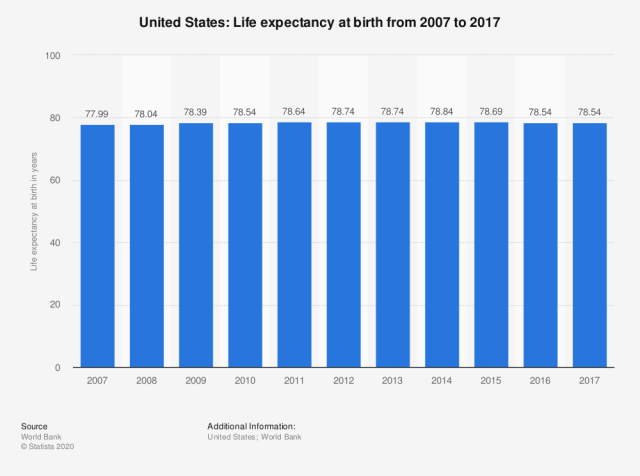
Across us counties, life expectancy in 2007 ranged from 65. 9 to 81. 1 years for men and 73. 5 to 86. 0 years for women. When compared against a time series of life expectancy in the 10 nations with the lowest mortality, us counties range from being 15 calendar years ahead to over 50 calendar years behind for men and 16 calendar years ahead to over 50 calendar years behind for women.
County life expectancy for black men ranges from 59. 4 to 77. 2 years, with counties ranging from seven to over 50 calendar years behind the international frontier; for black women, the range is 69. 6 to 82. 6 years, with counties ranging from eight to over 50 calendar years behind. Between 2000 and 2007, 80% (men) and 91% (women) of American counties fell in standing against this international life expectancy standard.
Life Expectancy in the US Increases for First Time in 4 Years
The crisis for social security. This same issue is playing out in the social security program. It was introduced in 1935. At that time, the average life expectancy was 60 years of age. By 2006 the average male was expected to live to age 74 and the average female to age 79. This means that over the years, more and more people were collecting social security simply because people were living longer. That is one of the things that has caused social security to begin running out of money. The social security plan has had to evolve to remain solvent. One strategy was to allow people to retire at age 62 with reduced benefits or at age 65 with full benefits.
Life expectancy increased for the first time in four years in 2018, the federal government said on Thursday, raising hopes that a benchmark of the nation’s health may finally be stabilizing after a rare and troubling decline that was driven by a surge in drug overdoses.
Life expectancy is the most basic measure of the health of a society, and declines in developed countries are extremely unusual. But the united states experienced one from 2015 to 2017 as the opioid epidemic took its toll, worrying demographers who had not seen an outright decline since 1993, during the aids epidemic.
An uptick in what has become known as “deaths of despair” — younger people dying from overdoses, suicide, and alcoholism — has drawn considerable attention from politicians and policymakers.
Many People Reach 22 Years Old Before They Can Leave Home
Medicaid, the government insurance program, covered care for a 22 year old who said:
“It’s like I’m 22 and I’ve finally made it out of my parents’ house, embracing life for the first time. I’m learning how to live. ”
The last time life expectancy in the united states flatlined for several years was in the 1960s, when the mass habit of smoking, particularly among men, began showing up in the mortality statistics, said dr. Samuel Preston, a demographer at the University of Pennsylvania. But from 1968 to 2010, life expectancy went up by an average of about two years a decade, he said, a substantially slower rate than in European countries, but twice as fast as the increase in 2018.
Recent Rise is Welcome!
Life expectancy at birth rose to 78. 7 years in 2018 from 78.
No doubt about it, obesity and all the related physical problems that come with obesity are causing some serious issues for us and our health. Now more than ever, it's critical that we take the time to exercise and educate ourselves on healthy eating! obesity is the problem, and we can be part of the solution!
Researchers at Tuft's University have studied aging. They have come up with five factors, which they call biomarkers, that can help people live longer and improve the quality of their life. Number one is diet. As the body ages, it requires fewer calories and this needs recognition.
A Historic Outlook on United States Life Expectancy at Birth
The loss in the Mexican-American war had an upside for Mexico. The payment for land by the united states stabilized their economy; the liberals and conservatives stopped fighting each other and closed ranks in defense of their common Spanish heritage.
It unified the country with the gringos as the common enemy. Still, 90 percent of the population was rural; literacy stood at 10 percent; life expectancy only 24 years. At mid-century, there were rich landowners, who by astute business practices and shrewd political maneuvering, had amassed huge holdings. A mere 17 haciendas encompassed 16 million acres. Santa Anna was appointed to the presidency again in 1853. He asked to be addressed as most serene highness. His highness was overthrown in 1855 by a group of young liberals, led by an Indian lawyer: Benito Juarez.
Drug overdoses accounted for a relatively small amount of the life expectancy gap between health in rural Appalachia and the rest of the country, at least through the end of the study in 2013.
I will take advice from these people because their average life expectancy is age 92 and my friend at 107 is my hero. Your heroes lived in ignorance and hard times.
Now read our original article on this page back in 2011:

First published Mar 17, 2011:
Life Expectancy in US at Record High
Life expectancy in the US has risen to a new high of 78 years and 2 months, according to a statistical analysis released by the Centers for Disease and Control, for 2009.
Life expectancy for men was 75.7 years and 80.6 years for women, both up slightly from 2008.
Life expectancy for whites stood at 78.6 years in 2009, compared with 74.3 years for blacks.
Deaths were down for a range of causes, from heart disease to homicide. No one simple explanation can be put forward for the increase in life expectancy, but that isn’t surprising when you consider all the myriad of things that affect our lives and our health. High on the list must be improved medical treatment and vaccination levels. Plus, public health measures that have had some success in reducing smoking may well be impacting this.
Heart disease has been and remains the top killer.
The data has been provided by the CDC based on the life expectancy for a baby born in 2009.
United States life expectancy has been tending to increase since at least the 1940s, although some years it has held steady, and a few occasions it has dropped.
Life expectancy is a common measure of population health in general and is often used as a summary measure when comparing different populations (such as for international comparisons). For example, high life expectancy indicates low infant and child mortality, an aging population, and a high quality of healthcare delivery.
Don’t confuse life expectancy with life span. Both life expectancy and longevity are averages and are distinct from life span. Life span refers to the number of years that humans could live under ideal conditions. Life expectancy is by definition an arithmetic mean.
We all like to hear that life expectancy is being extended. We like it less when we seek to take up our pensions, and we realize that there is less per pension money to go round when it needs dishing out to more people who are still living to keep claiming their pensions. Nevertheless, the effect on pensions only comes when the remaining number of years a person is expected to live, based on life expectancy tables issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), are revised.
Many people say that “full health”- adjusted life expectancy is a better measure to consider than that just of life expectancy because it introduces the concept of quality of life. Health-adjusted life expectancy is defined as the number of years in full health that an individual can expect to live given the current morbidity and mortality conditions.
The cost and quality of health care for the old and poor vary between states in America. Some states, like Massachusetts, have universal health coverage, but others don’t.
Data on persons enrolled in the National SCI Database suggests that the causes of death that appear to have the greatest impact on reduced life expectancy for their study population are pneumonia, pulmonary emboli, and septicemia.
Rises in living standards and to health care quality across Europe have also led to increases in life expectancy at birth. In the EU's 27 nation-states, life expectancy at birth increased over the last 50 years by about 10 years. Improvements in medical techniques, again the availability of medical treatment, public health, and nutrition are thought to be the main reasons for increased overall average lifespan, in these countries.
Women are also generally better off than men; worldwide their life expectancy exceeds that of men by a few years. Women marrying a partner seven to nine years younger increase their mortality risk by 20 percent compared to couples where both partners are the same age. But the mortality risk of a husband who is seven to nine years older than his wife is reduced by eleven percent.
Americans may be living longer but they are certainly paying quite a few more dollars for treatment than many other countries. Americans work longer hours and get less help from the state when ill than almost any other reasonably wealthy industrialized country. Some have even commented that the US is the only country where employees are forced to go to work sick or get fired!


Thank you for your blog. Really thank you! Much obliged.